leeb rebound hardness test method|leebs hardness chart : solution • Meyer hardness test See more The majority of regulated medical waste can be treated through an autoclave. This may include soiled bandages, gauzes, personal protective equipment or other items that are . See more
{plog:ftitle_list}
Autoclave valves are complemented by a complete line of high pressure fittings .
The traditional methods are based on well-defined physical indentation hardness tests. Very hard indenters of defined geometries and sizes are continuously pressed into the material under a particular force. Deformation parameters, such as the indentation depth in the Rockwell method, are recorded to give . See moreThe Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT) invented by Swiss company Proceq SA is one of the four most used methods for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large . See moreDepending on the probe (“impact device”) and indenter (“impact body”) types that vary by geometry, size, weight, material and spring force, . See more• Meyer hardness test See more
The Equotip (later on also called simultaneously as Leeb method) rebound hardness test method was developed in the year 1975 by Leeb and Brandestini at Proceq SA to . See more• German standards and specifications:• American standards:• Official international standards projects:• Official . See more• http://grhardnesstester.com/blog/methods-testing-hardness-steel/• https://www.baq.de/template.cgi?page=service_infos_ueber_messverfahren&rubrik=&id=&lang. The Leeb hardness testing, otherwise called as Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT), is considered as one of the four commonly used methods to test the hardness of the .
The Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT) invented by Swiss company Proceq SA is one of the four most used methods for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large workpieces (mainly above 1 kg).The Leeb hardness testing, otherwise called as Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT), is considered as one of the four commonly used methods to test the hardness of the metal. It is a type of non-destructive testing used to inspect large sized workpieces weighing above 1 kg. The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The results obtained are indicative of the strength and dependent on the heat treatment of the material tested.Another well-known principle for portable hardness testers is the rebound method. The DynaMIC and DynaPOCKET (Krautkramer), for example, measure the velocity of a propelled impact body directly before and after the impact onto the test material’s surface.
The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The results obtained are indicative of the strength and dependent on the heat treatment of the material tested.Determination of the hardness of metallic materials according to Leeb is defined in the ISO 16859 and ASTM A956 standards. In this dynamic test method, the ratio of rebound velocity to impact velocity of a moving impactor is used to determine the hardness. Governed by the ASTM A956/A956M standard, this method utilizes the Leeb hardness principle to deliver fast and accurate measurements essential in various applications, from quality control to on-site metal hardness evaluation.
ISO 16859-1:2015 covers the determination of a dynamic hardness of metallic materials using seven different Leeb scales (HLD, HLS, HLE, HLDL, HLD+15, HLC, HLG).
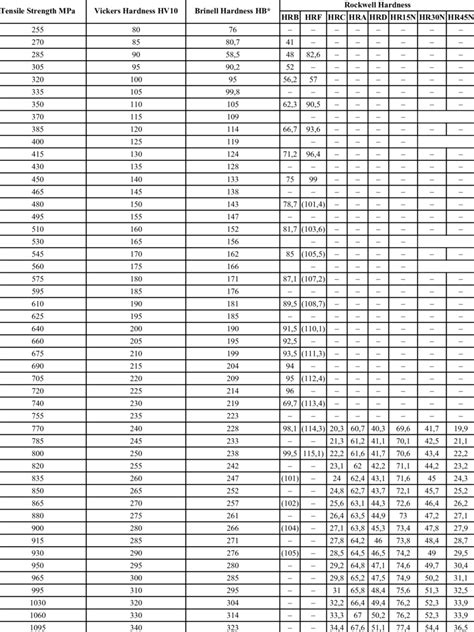
leebs hardness chart
There are two different physical methods which are particularly recognized in the practical field: the static Ultrasonic Contact Impedance (UCI) method and dynamic rebound hardness testing (Leeb). The decision as to which method is to be used mainly depends on the testing task.1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Leeb hardness of steel, cast steel, and cast iron (Part A), including the methods for the verification of Leeb hardness testing instruments (Part B), and the calibration of standardized test blocks (Part C).The Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT) invented by Swiss company Proceq SA is one of the four most used methods for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large workpieces (mainly above 1 kg).
The Leeb hardness testing, otherwise called as Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT), is considered as one of the four commonly used methods to test the hardness of the metal. It is a type of non-destructive testing used to inspect large sized workpieces weighing above 1 kg. The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The results obtained are indicative of the strength and dependent on the heat treatment of the material tested.Another well-known principle for portable hardness testers is the rebound method. The DynaMIC and DynaPOCKET (Krautkramer), for example, measure the velocity of a propelled impact body directly before and after the impact onto the test material’s surface.The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The results obtained are indicative of the strength and dependent on the heat treatment of the material tested.
Determination of the hardness of metallic materials according to Leeb is defined in the ISO 16859 and ASTM A956 standards. In this dynamic test method, the ratio of rebound velocity to impact velocity of a moving impactor is used to determine the hardness. Governed by the ASTM A956/A956M standard, this method utilizes the Leeb hardness principle to deliver fast and accurate measurements essential in various applications, from quality control to on-site metal hardness evaluation.ISO 16859-1:2015 covers the determination of a dynamic hardness of metallic materials using seven different Leeb scales (HLD, HLS, HLE, HLDL, HLD+15, HLC, HLG).There are two different physical methods which are particularly recognized in the practical field: the static Ultrasonic Contact Impedance (UCI) method and dynamic rebound hardness testing (Leeb). The decision as to which method is to be used mainly depends on the testing task.
leeb rebound hardness test wikipedia
leeb hardness tester principle
leeb hardness calculator
To be effective, the autoclave must reach and maintain a temperature of 121° C for at least 30 minutes by using saturated steam under at least 15 psi of pressure. Increased cycle time may .
leeb rebound hardness test method|leebs hardness chart